The back muscles, often overlooked but essential for posture, movement, and stability, deserve a comprehensive understanding. This guide delves into the anatomy, biomechanics, strengthening, injuries, and advanced techniques related to back muscles, empowering you with knowledge for optimal back health and fitness.
From understanding the major muscle groups and their functions to mastering exercises for strengthening and conditioning, this guide provides a roadmap for building a strong and healthy back.
Back Muscles: Anatomy, Function, and Importance
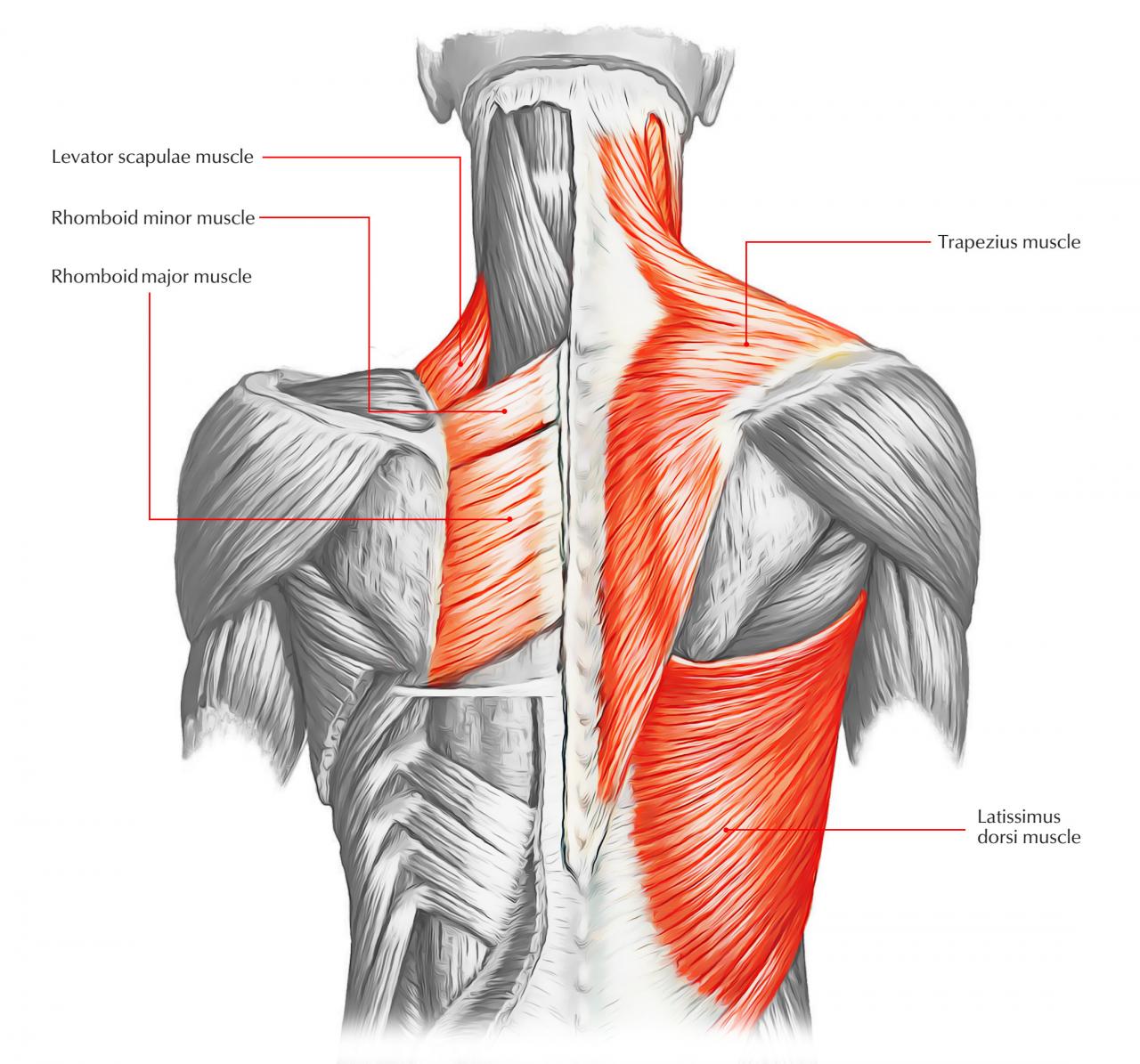
The back muscles are a complex and essential group of muscles that play a vital role in posture, movement, and stability. They support the spine, protect the internal organs, and allow for a wide range of motions.
Definition and Anatomy of Back Muscles
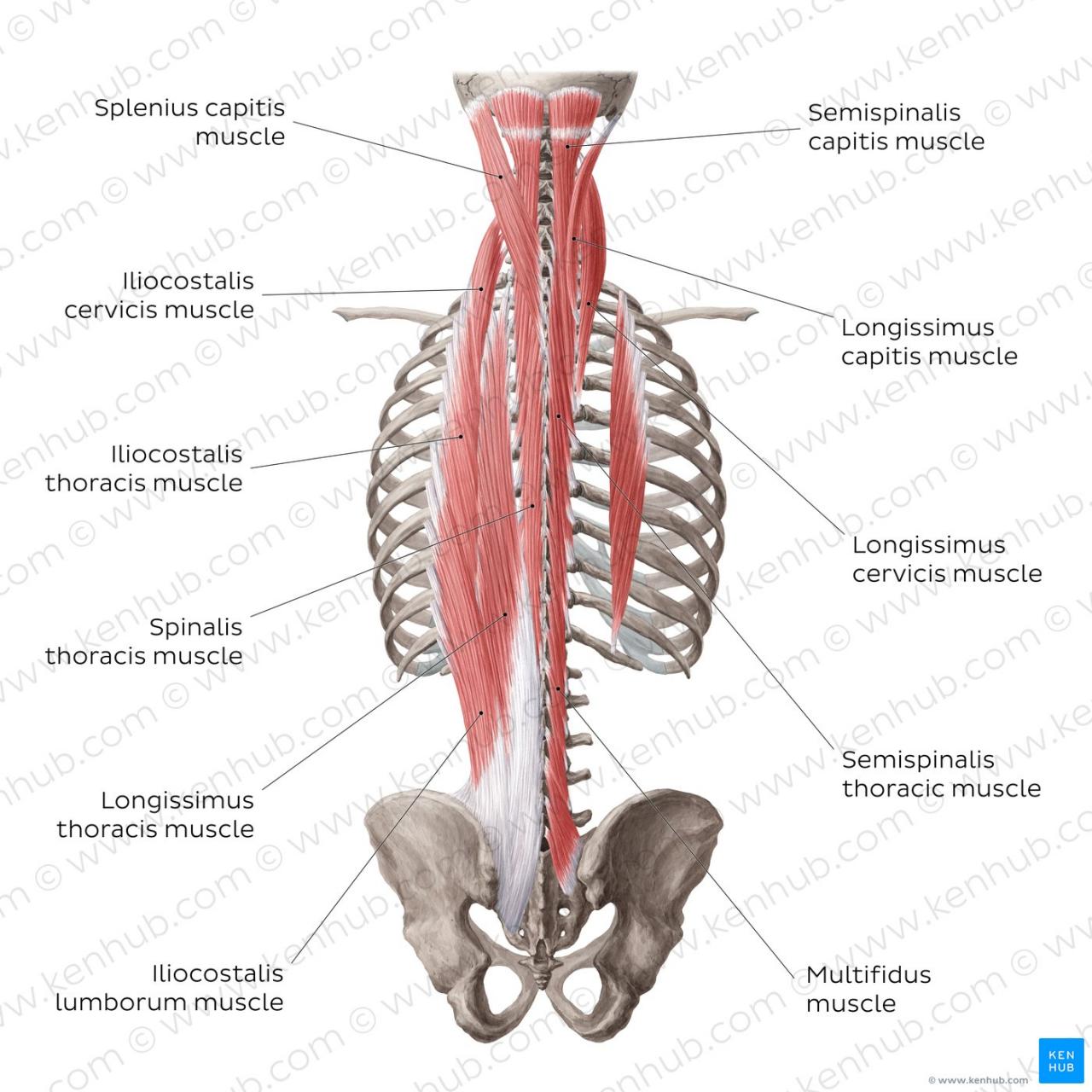
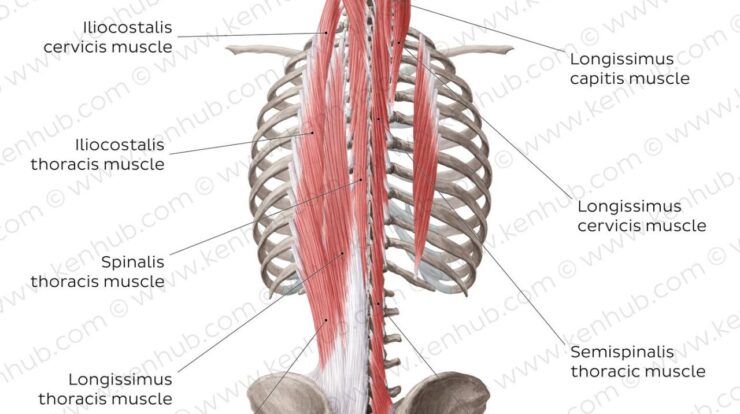
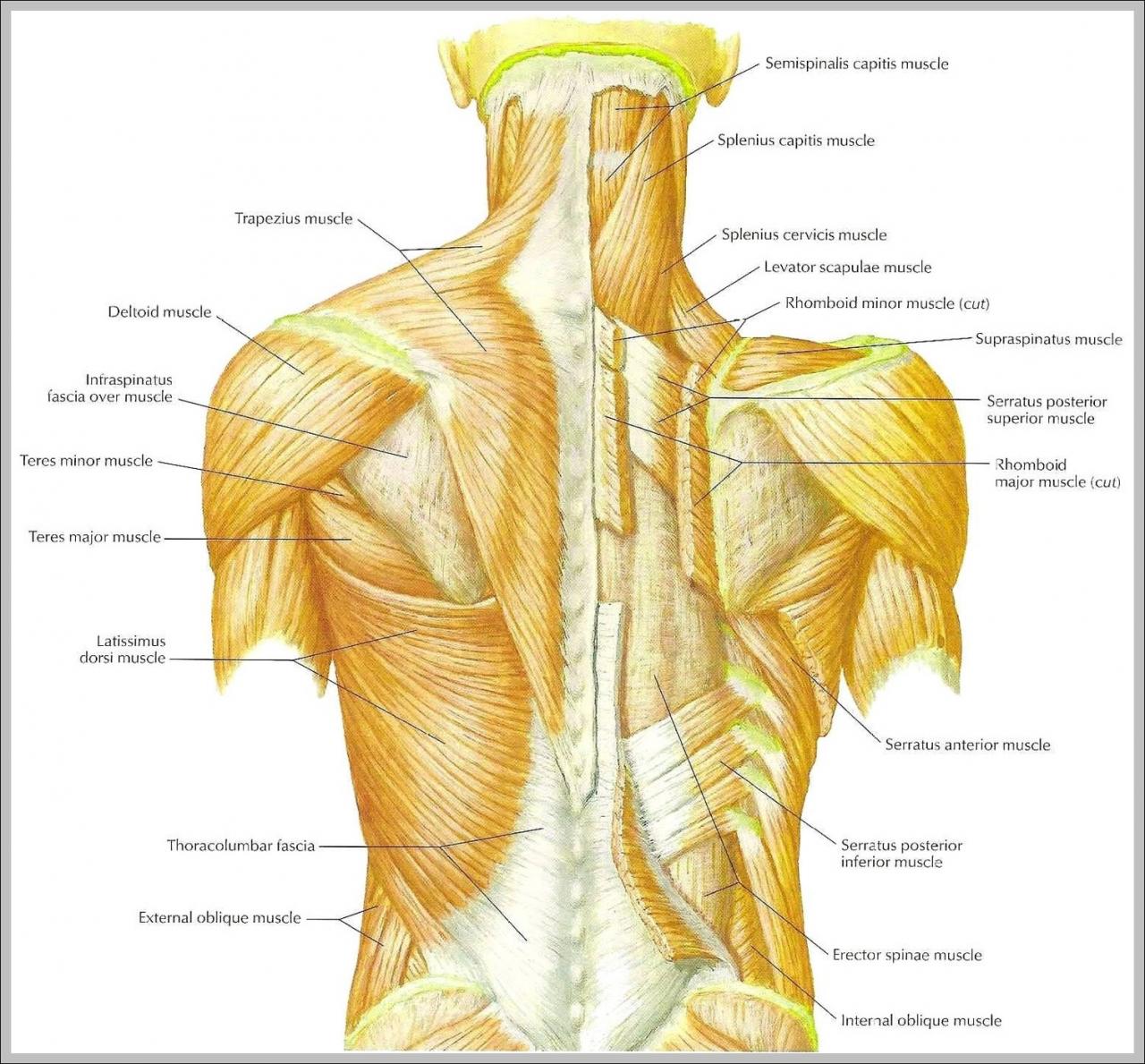
The back muscles can be divided into three main groups: the superficial muscles, the intermediate muscles, and the deep muscles. The superficial muscles are located closest to the skin and include the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, and rhomboids. The intermediate muscles are located beneath the superficial muscles and include the serratus posterior superior and serratus posterior inferior.
The deep muscles are located deepest and include the erector spinae, multifidus, and rotatores.
Each of these muscle groups has its own specific function. The superficial muscles are responsible for movements of the shoulder and arm, while the intermediate muscles are responsible for movements of the rib cage. The deep muscles are responsible for supporting the spine and controlling its movements.
Biomechanics of Back Muscles
The back muscles play a vital role in posture, movement, and stability. They work together to maintain the curvature of the spine, support the head and neck, and allow for a wide range of motions. The back muscles also help to protect the internal organs from injury.
Stiff and tight muscles can lead to back pain, as they can cause strain on the back muscles . Exercises to relieve lower back pain can help to stretch and strengthen these muscles, improving flexibility and reducing pain. Exercises to relieve lower back pain include gentle stretches, such as knee-to-chest stretches, and strengthening exercises, such as pelvic tilts.
Celebrating Mother’s Day is a special occasion to express gratitude to all moms. Sending happy mothers day wishes for all moms images can brighten their day and show appreciation for their love and support.
The back muscles are innervated by a number of nerves, including the spinal nerves, the brachial plexus, and the lumbar plexus. These nerves send signals to the muscles, which allow them to contract and relax.
Final Wrap-Up: Back Muscles
In conclusion, the back muscles play a crucial role in our physical well-being. By understanding their anatomy, biomechanics, and proper care, we can maintain a strong and healthy back throughout our lives. Whether you’re an athlete, an older adult, or simply seeking to improve your posture, this guide offers valuable insights and practical recommendations for achieving your back muscle goals.
FAQ Corner
What are the most common back muscle injuries?
Strains, sprains, and herniated discs are among the most common back muscle injuries.
How can I prevent back muscle injuries?
Maintaining good posture, practicing proper lifting techniques, and engaging in regular exercise can help prevent back muscle injuries.
What exercises are best for strengthening back muscles?
Exercises such as deadlifts, rows, and pull-ups are effective for strengthening back muscles.
Back pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including stiff and tight muscles. How can stiff and tight muscles result in back pain? The back muscles are responsible for supporting the spine and providing mobility. When these muscles become tight or stiff, they can put pressure on the spine and nerves, causing pain.
Exercises to relieve lower back pain can help to stretch and strengthen the back muscles, which can help to reduce pain and improve mobility. If you are experiencing back pain, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.